Scleroglucan
Scleroglucan is a water soluble, nature-derived polysaccharide produced by fermentation of the filamentous fungus Sclerotium rolfsii. It is a highly versatile ingredient, which improves the sensory characteristic of personal care products. Scleroglucan has rheological properties, and unlike most natural and synthetic gums, has high thermal stability, is resistant to hydrolysis and retains skin moisture.
Brand name
- ACTIGUM™CS sclerotium gum
- ACTIGUM™VSX sclerotium gum and xanthan gum
Applications
Scleroglucan can be used in hair, skin and sun care, bath and body products and color cosmetics.
- Skin care: lotions, creams, face masks and packs
- Sun care: sun protection lotions
- Bath and shower: shower gels and body washes
- Color cosmetics: make-up, mascaras and eyeliners
- Hair care: shampoos and conditioners
- Shaving foam
Functionalities
- Moisturizer
- Sensory improver
- Thickening agent
- Stabilizer
- Cold-soluble
- Electrolyte tolerant
- Forms fluid gels with very high and unique suspension properties
- Sparkling clarity
- Process flexibility and tolerance
- Excellent and exceptional suspension for insoluble solids and oil droplets
- Highly effective at low concentrations
- Shear reversible behavior
- Excellent emulsifier and foam stabilizer
- Excellent stability in extremely high conditions
Chemistry
The chemical structure consists of beta-1,3-D-glucose residues with one beta-1,6-D-glucose side chain every three main residues. Although it produces aqueous solutions with a very high viscosity, its molecular weight is very high: Mw = 1,000,000 Da.
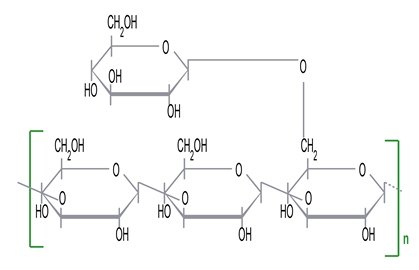
Its remarkable rheological properties and stability over a wide range of pHs, salinities, and temperatures make this neutral non-ionic polysaccharide suitable for a number of applications.
High thermal stability: Unlike most natural and synthetic gums, high temperature has little effect on the viscosity of a scleroglucan solution. Below 10°C (50°F), the solutions have a semi-gelled appearance that can be eliminated by shaking or heating. Solutions of scleroglucan may be sterilized by heating them at 121°C (250° F) for 20 hours without affecting their viscosity.
Yield value and anti-settling properties: Solutions of scleroglucan have a pseudo-plastic behavior with a high yield value, resulting in solutions of high-suspending power with good pouring properties. Because of its high yield value, it is extremely effective in holding particles in suspension, in static as well as in dynamic conditions, without any risk of sedimentation.
Excellent compatibility: Due to its non-ionic nature, acids and alkalis do not affect scleroglucan over a wide pH range (2.5 to 12), and so do not most electrolytes. It is compatible, without synergism, with most of the other thickeners such as guar gum, locust bean gum, alginate, gelatin, xanthan gum, carrageenans, and cellulose derivatives. It is also compatible with most widely used surfactants such as sulfates, sulfonates and quaternary ammonium salts. Scleroglucan remains soluble in mixtures containing up to 50 percent of polyols and glycols.
