Carrageenans
 Cargill offers one of the widest ranges of commercially available carrageenans, employing proven production processes and using a large variety of different types of red seaweeds (Rhodophyceae) from the Gigartinales group. The main varieties of seaweed used are:
Cargill offers one of the widest ranges of commercially available carrageenans, employing proven production processes and using a large variety of different types of red seaweeds (Rhodophyceae) from the Gigartinales group. The main varieties of seaweed used are:
- Gigartina (France, Argentina/Chile, Morocco)
- Chondrus (France, North Atlantic)
- Iridaea (Chile)
- Eucheuma (Philippines/Indonesia/East coast of Africa)
Together with Cargill's recognized formulation expertise, this enables the formulation of commercial carrageenan products tailored to very specific needs in different applications.
Applications
Carrageenans are used as thermoreversible gelling, thickening and stabilizing agents in a wide variety of applications, mainly in the food industry. Their specific interactions with proteins and their synergetic effects with other hydrocolloids such as locust bean gum and konjac gum makes them very suitable for use in:
-
Dairy
- Stabilization of chocolate drinks and creams
- Dairy desserts, like gelled milks, flans, multi-layered desserts, mousses
- Cheese specialties
-
Fruit
- Fruit preparations for yogurt
- Water jellies, glazes
-
Ice cream
- In combination with guar gum, locust bean gum and alginates
-
Meat
- Brine injections (hams, poultry)
- Fat reduction (hamburgers)
- Canned foods: in combination with locust bean gum for human and pet food
-
Non-food applications
- Toothpaste and cosmetics
- Air fresheners
-
Pharmaceuticals & neutraceuticals
- Excipients
- Soft gels
-
Powder products
- Homemade flans
- Dessert, custard and bakery creams
Brands
Cargill's carrageenan products are available under the following trademarks:
- Satiagel™- Gelling extracts: food and pharma grades
- Satiagum™ - Thickening extract: food and pharma grades
- Aubygel™ - Gelling PES: food grades
Certification System
Cargill's carrageenan products are Kosher and Halal certified. All regional, national and international certifications are issued by well known official certification bodies and available upon request.
Depth of Expertise
With over 50 years of experience, we have acquired a thorough knowledge of all relevant technologies in carrageenan manufacture and formulation. Our expertise is based on our knowledge of both the specific characteristics of carrageenans and the requirements of a broad spectrum of industries and functionality, resulting in specially tailored products optimized for different applications.
The manufacturing of carrageenan in all its varieties requires a high level of production expertise.
Cargill's worldwide sourcing of seaweed ensures the supply of a broad spectrum of properties and functionalities in its carrageenan raw materials.
The plants use the latest extraction, separation and drying technologies and are designed to produce the full range of carrageenans (refined alcohol process, refined KCl process and P.E.S.).
Each processing stage is performed under tight quality controls. The reproduction of commercial products is ensured by strict formula controls and exact monitoring conditions.
Functionality
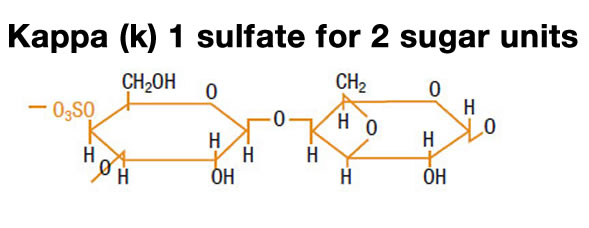
Carrageenans are polysaccharides made of galactose units with different levels of sulfate substitution. Their sulfate content is between 15 and 40%. Many red seaweeds contain mixtures of such polysaccharides. In carrageenans, all the galactose units occur in the D form.
Depending on the number of sulfate groups per galactose molecule, three types of carrageenan molecules can be distinguished:
- Kappa carrageenan: 1 sulfate unit for two galactose molecules
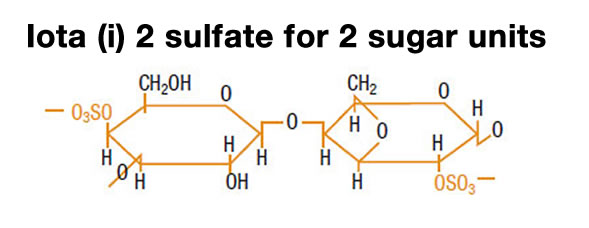
- Iota carrageenan: 2 sulfate units for two galactose molecules
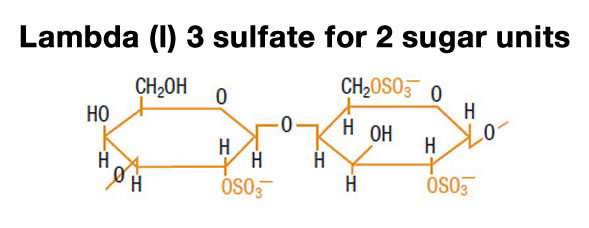
- Lambda carrageenan: 3 sulfate units for two galactose molecules
It should be noted that carrageenan macromolecules are not homogeneous chains made up of the same repetitive units, but they are heterogeneous, either due to differing molecular structures within the chains or due to differing chains within the seaweed. For example, some carrageenans extracted from South American seaweeds are kappa and iota hybrids, also called kappa 2 or weak kappa carrageenans.
Lambda carrageenan is cold soluble and acts simply as a thickening agent.
Gelling carrageenans require heat treatment for dissolution. When cooling down, the macromolecules have a tendency to spontaneously associate, thus creating junction zones required for a gel.
Being very diverse, carrageenans can broadly be classified into three main “ideal” types of carrageenan, split into two groups:
- Gelling carrageenans: products rich in kappa and iota fractions
- Thickening carrageenans: products rich in lambda fractions
Gelation of kappa carrageenan is particularly enhanced by the potassium ion. It induces gel formation at very low concentrations. Because of its small hydro-dynamic size when hydrated, the potassium ion fits into the coil and partially neutralizes the sulfate groups. Thus, the double-helices can cluster together and form aggregates that create a strong, brittle, gel.
 The iota carrageenan network is formed by a series of double-helices and kinks that form a transparent, elastic gel. This loosely connected network can easily be destroyed by mechanical action. However, it reforms quickly once the mechanical action has stopped. This property is called " thixotropy " and is very useful in certain applications, such as cold-filled dairy desserts.
The iota carrageenan network is formed by a series of double-helices and kinks that form a transparent, elastic gel. This loosely connected network can easily be destroyed by mechanical action. However, it reforms quickly once the mechanical action has stopped. This property is called " thixotropy " and is very useful in certain applications, such as cold-filled dairy desserts.
 Lambda carrageenans can be used as thickening agents only, since due to electrostatic repulsion, the chains of lambda carrageenan do not have a tendency to self-associate. They can thus be easily separated from each other.
Lambda carrageenans can be used as thickening agents only, since due to electrostatic repulsion, the chains of lambda carrageenan do not have a tendency to self-associate. They can thus be easily separated from each other.
Manufacturing
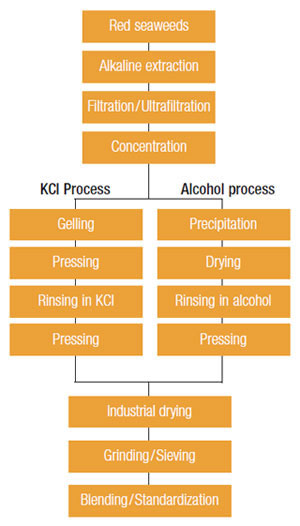 Industrial production of refined carrageenan consists of three main steps:
Industrial production of refined carrageenan consists of three main steps:
- Extraction in alkaline conditions
- Purification by separating the gum from insoluble impurities
- Carrageenan recovery (precipitation in alcohol or gelation of filtrate in presence of potassium chloride, drying then milling)
Semi-refined carrageenan, or P.E.S., differs from refined carrageenan in two main respects:
- Firstly, the only permitted raw material for P.E.S. is Eucheuma Seaweed.
- Secondly, it is obtained by simple alkaline treatment (no extraction and no filtration).
Partners in Success
In Cargill’s carrageenan business, we take time to understand your specific needs in order to provide solutions, not just products. Worldwide customers recognize this and benefit from our:
- Modern plants using the latest extraction, separation and drying technologies
- Wide range of applications from thickening to gelling properties
- Specialty and customized products
- Industry-specific solutions designed for the particular needs of the meat, dairy, confectionery, bakery and personal care industries
Helping your business succeed by differentiating you from your competitors is our primary goal.
Production Sites
Cargill started its carrageenan production in 1956 in Baupte, Normandy, France using the local seaweed (Chondrus Crispus).
Today, Cargill's production facilities in France and the Philippines are amongst the most advanced in the world. Highly sophisticated manufacturing processes are employed to ensure a fast and flexible response to customers' requirements.
- Cargill manufactures carrageenans at the following sites:
- Baupte (France) - ISO 9001: 2000
- Canlubang (Philippines) - ISO 9001: 2000
Each production batch is produced under controlled conditions to ensure consistent performance in application in compliance with our ISO certifications.
Regulatory Status
European legislation clearly distinguishes carrageenan (E 407) from Processed Eucheuma Seaweed (P.E.S.) (E 407a - a semi refined carrageenan as described below), using the acid insoluble matter as the main criteria for differentiation.
FAO/WHO - Codex Alimentarius
Carrageenan and P.E.S. have been given an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of “not specified” by the FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA).
European Union
Carrageenan (E 407) and P.E.S. (E 407a) are listed in Annex I of the European Parliament and Council Directive 95/2/EC of 20th February 1995 on food additives, and may be used at “quantum satis” in many food categories.
United States
The FDA recognizes carrageenan and P.E.S. as permitted for direct addition to food for human consumption in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 21, § 172.620).
Cargill's global team of regulatory and food law experts will be glad to provide assistance on regulatory, nutrition-related claims and food law-related issues.
Some Cargill products are only approved for use in certain geographies, end uses, and/or at certain usage levels. It is the customer's responsibility to determine, for a particular geography, that (i) the Cargill product, its use and usage levels, (ii) the customer's product and its use, and (iii) any claims made about the customer's product, all comply with applicable laws and regulations.
